[ad_1]
By Edward Mitchard, professor of worldwide change mapping on the College of Edinburgh’s Faculty of GeoSciences, and chief scientist of service supplier House Intelligence.
Current claims across the effectiveness of rainforest carbon credit are being hotly debated proper now. And rightly so. Firms have reportedly paid over $1 billion for these credit, and they’re getting used to offset ‘actual’ emissions. So, in the event that they’re not real, that’s a large downside for local weather motion.
The stubbornly excessive charge of worldwide tropical deforestation is a tragedy of our age: by 2021, we destroyed round 23% of the tropical forest that remained within the 12 months 2000 [1]. That is regardless of repeated commitments from nations and multi-national teams to halt deforestation, most just lately with the Sustainable Growth Targets (SDGs), which aimed to cease deforestation by 2020. This has merely not occurred. Deforestation continued on the identical tempo in 2021, 2020, and multiples years prior.
[1] https://forobs.jrc.ec.europa.eu/TMF/index.php – Printed paper C. Vancutsem, F. Achard, J.-F. Pekel, G. Vieilledent, S. Carboni, D. Simonetti, J. Gallego, L.E.O.C. Aragão, R. Nasi. Lengthy-term (1990-2019) monitoring of forest cowl adjustments within the humid tropics. Science Advances 2021
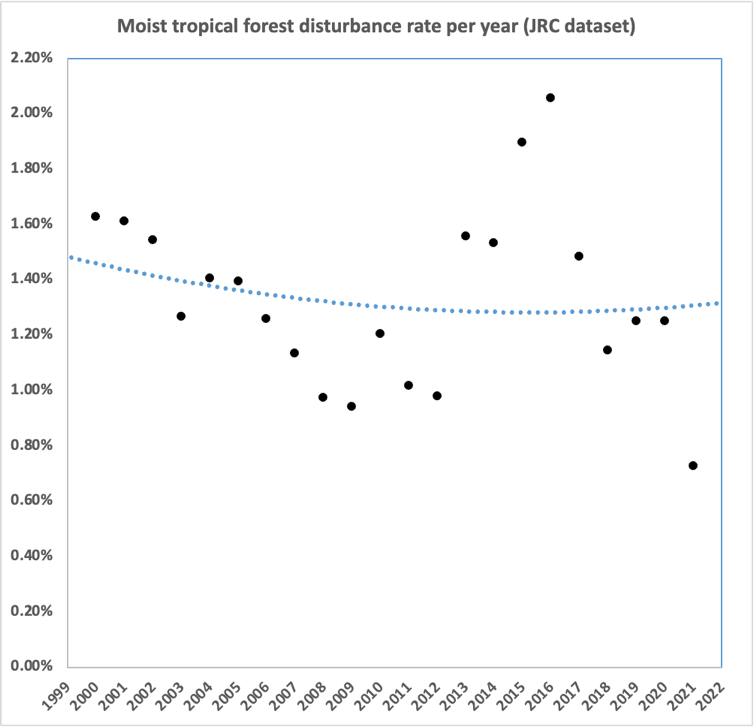
Annual moist tropical forest disturbance. Word annual variability partly on account of cloud cowl and knowledge availability. Long run must be dependable. Knowledge from https://forobs.jrc.ec.europa.eu/TMF/
Decreasing Emissions from Deforestation and forest Degradation (REDD+) tasks, largely licensed below the Verified Carbon Normal (VCS) run by Verra, present a mechanism for people and firms within the developed world to preserve tropical forests, and the valuable biodiversity and carbon they retailer.
Carbon offsets will not be a panacea, and won’t cease local weather change: however they’re a method for corporations and people who’ve unavoidable emissions to take that carbon again out of the ambiance, and do some good to the world’s poorest folks and most biodiverse forests whereas doing so.
I’ve visited a few of these tasks and talked to native communities throughout Peru, Uganda, and Tanzania. I’ve seen first-hand how they bring about cash and alternatives to a number of the world’s poorest folks, and genuinely cease the strain on the forests. I’ve additionally been concerned within the tortuous means of gaining approval for a few of these tasks. This includes tons of of pages of paperwork, 1000’s of bushes measured, countless questions from the undertaking auditors, and using sophistic satellite tv for pc datasets.
With this in thoughts, I used to be shocked to learn the Guardian’s current story claiming that over 90% of rainforest carbon credit are ineffective, so I got down to higher perceive the three research behind the reporting.
On first look the research seem rigorous: two have gone via peer evaluate, and the third has an analogous creator group and strategies to the others. Nevertheless, my instant thought is that they don’t cowl many tasks. There are 104 Verra validated REDD+ tasks, with many extra in improvement, however these research solely thought-about 40. It’s subsequently clear that scientists didn’t write the headline that “greater than 90% of rainforest carbon credit … are nugatory”, given fewer than half of the tasks have been studied.
As an skilled in making maps of deforestation for REDD+ tasks, the following factor I went to verify was what satellite tv for pc knowledge and evaluation strategies the authors used to map deforestation. To my disappointment, I found all of them used pre-published, large-scale datasets reliant on NASA Landsat satellite tv for pc knowledge: the current (non-peer reviewed) research led by Thales West used the World Forest Change dataset (which ‘powers’ World Forest Watch), the older Brazil-focused West research makes use of a Brazilian House Company (INPE)-derived dataset known as PRODES, and the research led by Guizar-Coutiño makes use of a product centered on moist tropical forest produced by the EU’s JRC (used to make the determine above).
Whereas every has their strengths, it’s well-known that broad datasets will not be vastly correct on the particular person undertaking degree. REDD+ tasks want granular, regionally calibrated knowledge and so tasks demand skilled inner groups or using exterior corporations. Such maps typically make use of Artificial Aperture Radar knowledge or different, optical satellite tv for pc datasets which can be the next decision than Landsat. Utilizing any of those worldwide datasets wouldn’t usually fulfill a validator following Verra’s strict necessities for its VCS methodology.
For instance, considered one of my PhD college students and I confirmed in a peer reviewed research how two of those datasets (World Forest Watch and PRODES) underestimated forest loss in Brazil [2]:
[2] https://iopscience.iop.org/article/10.1088/1748-9326/aa7e1e/meta
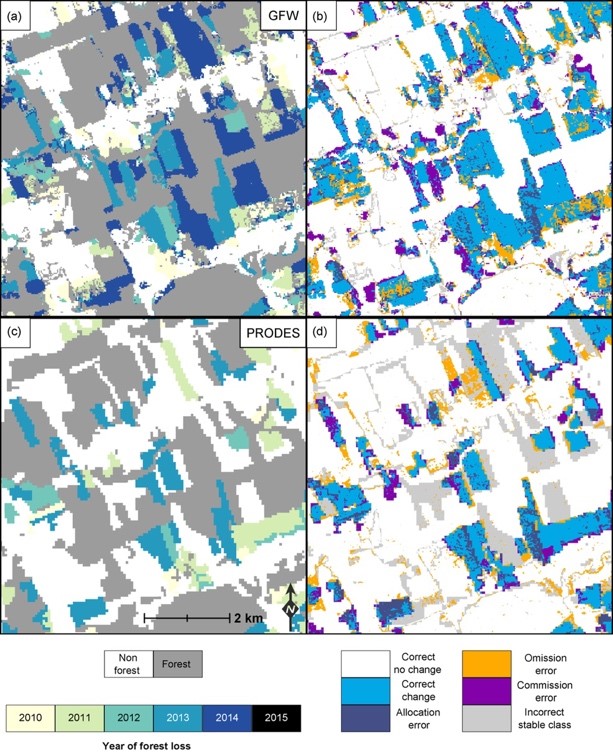
Different elements can intrude with measurement too. Cloudy and dry forest areas carry out particularly poorly, resembling these within the World Forest Change dataset being utilized by West [3].
[3] https://www.nature.com/articles/s41467-018-05386-z
GFW’s dataset solely makes use of optical satellite tv for pc knowledge, which is ok over tropical forest areas, however over drier areas it may be confused by grasses, grass fires, and bushes shedding their leaves. Artificial Aperture Radar knowledge, which is tougher to analyse, can overcome problems with cloudy circumstances and supply way more correct outcomes. This wasn’t utilized in any of the research, however many REDD+ tasks use such radar knowledge for this actual motive.
The 2 West papers then use a method known as ‘artificial controls’: this compares the tasks’ progress towards randomly chosen areas outdoors the undertaking space that maintain some similarity. If REDD+ tasks are working effectively then, when utilizing this methodology, the deforestation charges in these management websites ought to match the undertaking ‘baselines’, whereas the charges within the outdoors space must be a lot decrease. A undertaking’s baseline is ready on the outset of the undertaking; it’s the predicted deforestation charge over the following ten years if the undertaking didn’t occur.
Whereas this appears like a smart method, it is rather tough to search out appropriate management areas to make these comparisons and I see that the authors excluded tasks the place they may not discover good matches, regardless of these being a number of the finest performing tasks (e.g. the Southern Cardamom undertaking in Cambodia, which has few matching websites exactly as a result of it’s successfully defending a singular massive block of forest with no equal elsewhere in Cambodia). REDD+ tasks should undergo rigorous processes that comply with a strict methodology to pick out their management areas. These are additional chosen primarily based on native circumstances and analysis, which had been additionally excluded, not simply evaluation of worldwide datasets.
All three papers take a look at their strategies of choosing management areas by evaluating websites earlier than the REDD+ tasks begin. This is a crucial comparability to do, because it checks whether or not the strategy works in precept. If the strategy labored, these strains would all match completely throughout the intervals being studied: however in all three research they don’t in each case. Because the determine beneath taken from the West (2023) paper reveals, there are large deviations in lots of instances. For instance, regardless that there aren’t any energetic REDD+ tasks on the time chosen, their evaluation suggests undertaking 1395 in Colombia, and tasks 1897 and 1775-2 in Zambia have carried out very poorly; in different instances the error is the opposite method. This implies their methodology of choosing matching areas is poor. Nonetheless they use this methodology to match the REDD+ tasks after they begin.
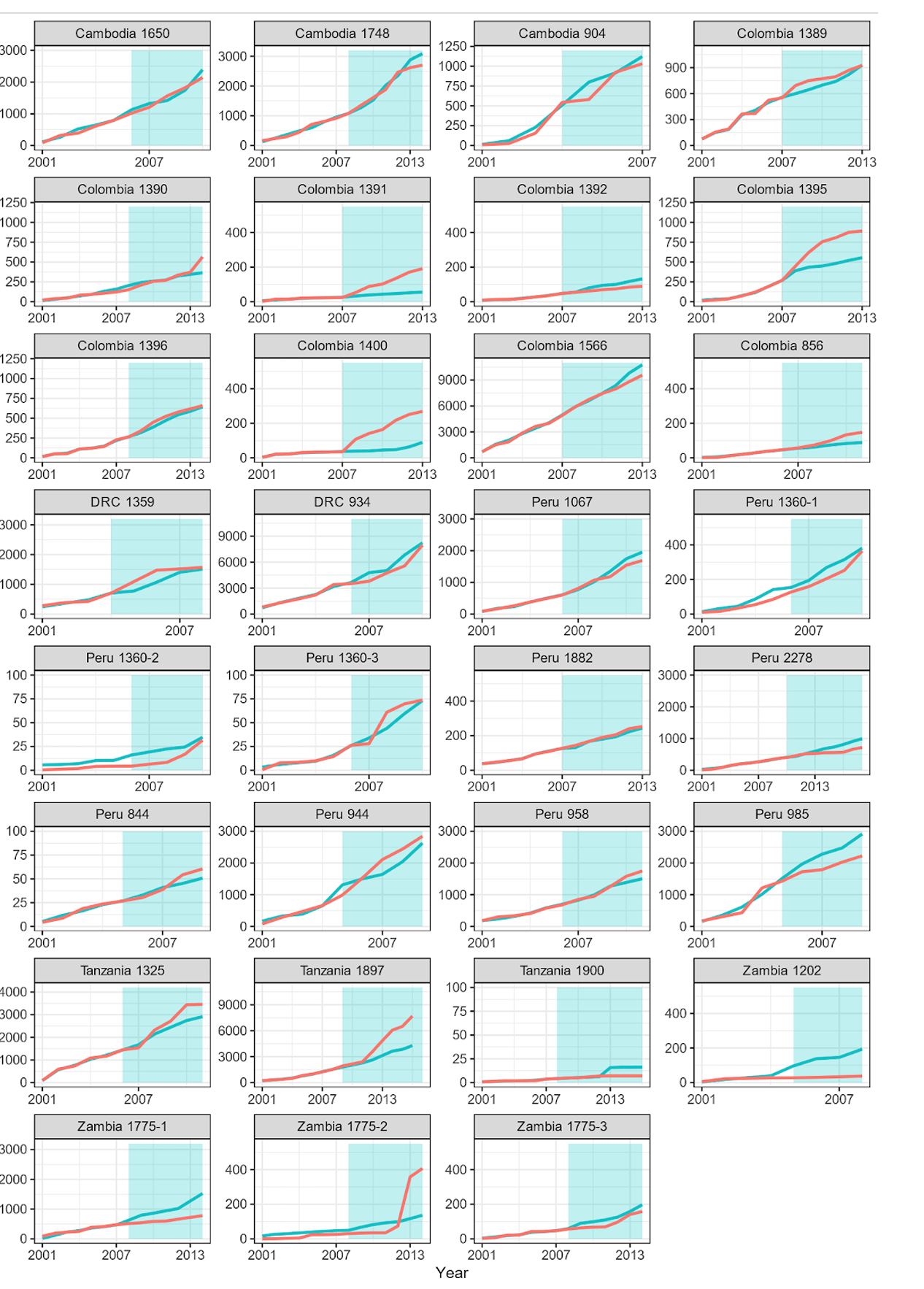
Pink strains are the deforestation charges within the undertaking websites, blue within the management areas, determine S2 from this paper [4]. They’re educated (i.e. matches chosen) on the white areas of the graphs, then examined on the blue areas.
[4] https://arxiv.org/abs/2301.03354
The significance of reporting REDD+ tasks precisely can’t be understated when the problem we’re dealing with is so immense: the conservation of tropical forests is integral to stopping the worst results of local weather change. This work is very advanced, and it requires steady scrutiny and enchancment (which is ongoing, e.g. see Verra’s exercise right here), however blanket evaluation and flawed reporting danger us shedding sight of what we all know is working. Put merely, no different mechanism at the moment exists to finance forest conservation at this scale, and we’re operating out of time.
Edward Mitchard is Professor of World Change Mapping on the College of Edinburgh’s Faculty of GeoSciences, and co-founder and chief scientist of House Intelligence, an organization that gives satellite-based maps to nature-based options tasks globally.
[ad_2]
Source_link












